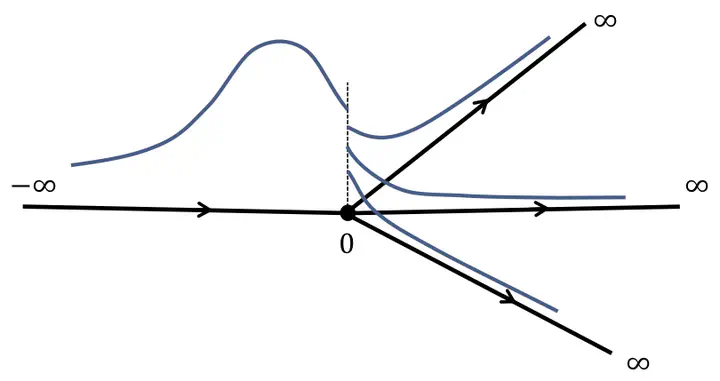
Abstract
When the coefficients of the cubic terms match the coefficients in the boundary conditions at a vertex of a star graph and satisfy a certain constraint, the nonlinear Schrödinger (NLS) equation on the star graph can be transformed to the NLS equation on a real line. Such balanced star graphs have appeared in the context of reflectionless transmission of solitary waves. Steady states on such balanced star graphs can be translated along the edges with a translational parameter and are referred to as the shifted states. When the star graph has exactly one incoming edge and several outgoing edges, the steady states are spectrally stable if their monotonic tails are located on the outgoing edges. These spectrally stable states are degenerate minimizers of the action functional with the degeneracy due to the translational symmetry. Nonlinear stability of these spectrally stable states has been an open problem up to now. In this paper, we prove that these spectrally stable states are nonlinearly unstable because of the irreversible drift along the incoming edge towards the vertex of the star graph. When the shifted states reach the vertex as a result of the drift, they become saddle points of the action functional, in which case the nonlinear instability leads to their destruction. In addition to rigorous mathematical results, we use numerical simulations to illustrate the drift instability and destruction of the shifted states on the balanced star graph.